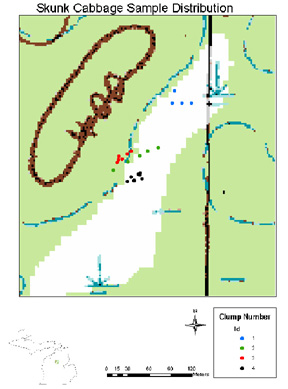
Skunk cabbage samples were taken from Lake Mitchell Swamp, Cadillac, Michigan. Samples were taken from clumps, which were designated as plants that could possibly have come from the same seed or underground vegetative growth and were less than six inches apart. A total of twenty-two clumps were sampled from, in four habitat sites. These sites and clumps can be seen on the map of the study area. The first site, on the edge of the swamp, was drier and dominated by tag-alder. The second site was in the middle of the open wetland so the habitat was much wetter and had both tag-alder and cattails intermixed. Located on higher ground and covered with aspen and grasses, the third site was the driest of the other three. The fourth site was located in the open wetland and surrounded by cattails. The clumps themselves are located from our original clump in site one. The vector and distance were taken from plant one, site one to plant two, site one. The second site was located from plant one, site one and then the clumps (plants) in site two were located off of plant one site two. Site three was then located off of plant one, site two and this procedure was done through site four.
We figured the best DNA samples could be found in the new shoots of the plant, so the top of one shoot from each plant was cut using a razor blade. Each sample was then placed in a zip-lock bag labeled with both site and clump number. The sample bags were then kept on ice in a cooler so that the samples did not deteriorate before we could get them back to the lab.
 DNA Extraction
DNA Extraction