1. Before you start this topic, you need to know the structure of nucleic acids, what a nucleotide is, how nucleotides are connected, and why nucleic acids have a direction.
2. Review the section on DNA replication in your textbook (page 210). Study figure 8.4 and review info about different DNA polymerases and their activities in the notes you took during lecture.
3. Bacterial cells typically have three polymerases. Study their names and properties in the notes you took during lecture. Then copy and fill in the table below. Once you have done that, check your answers by mousing over the word ANSWER below the table.

ANSWER
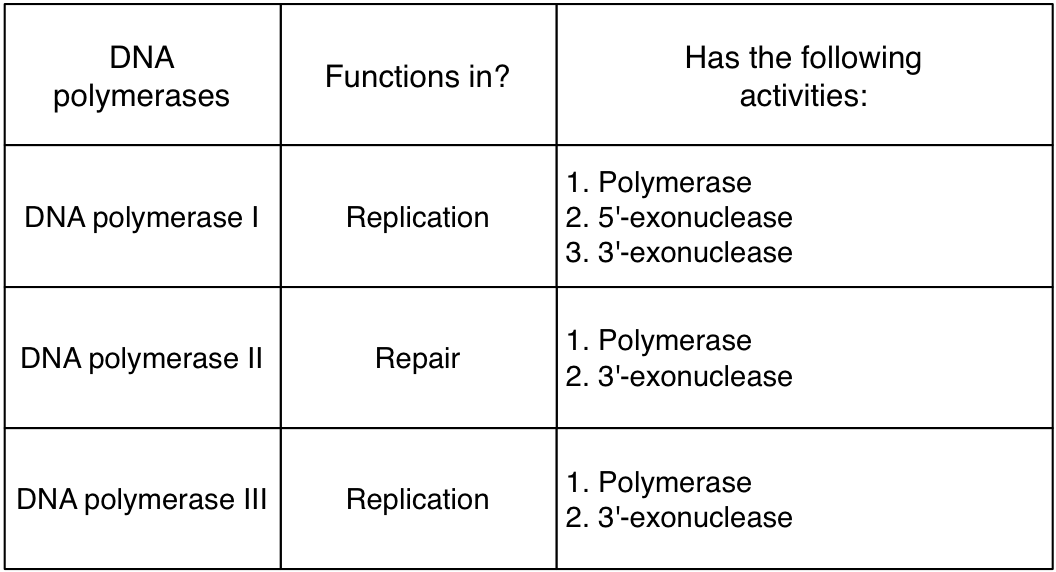
4. In the table below you filled in the different activities that DNA polymerases have. What exactly can those enzymes do and why do they have those activities? Study the notes you took during lecture. Then copy and fill in the table below. Once you have done that, check your answers by mousing over the word ANSWER below the table.

ANSWER

5. Now let's focus on DNA polymerase's most important function - the synthesis of new molecules of DNA. Review your textbook and notes you took during lecture. Once you have reviewed that material, you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How does DNA polymerase synthesize new DNA?
- What does DNA polymerase need to make new DNA molecules?
- Making new DNA strands requires energy (to make the bond between nucleotides). Where does that energy come from?
- How is the energy source for DNA synthesis related to the way in which DNA polymerases work (more specifically, at what end they are adding nucleotides)?
6. Study figure 8.4 in your text, as well as the slide that shows how DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA in your lecture notes. Once you have reviewed the info, close your book and notes and attempt to draw the steps of DNA synthesis on a piece of paper. Check your drawing against the lecture notes. Do it as many times as you need, until you are confident that you understand how new DNA is synthesized.
7. If you feel that you have mastered the concepts on this page, you can move to the next topic, which discusses the principles of DNA replication.